Search Engine Marketing (SEM) is a digital marketing strategy that involves promoting websites by increasing their visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs) through paid advertising. SEM primarily focuses on paid search advertising, commonly known as Pay-Per-Click (PPC) advertising, where advertisers bid on keywords relevant to their target audience.
Here’s how SEM works and some key components:
1 – Keyword Research
SEM begins with keyword research to identify the terms and phrases that potential customers are using to search for products or services related to your business. These keywords form the basis of your SEM campaigns.
2 – Campaign Setup
Advertisers create SEM campaigns using platforms like Google Ads (formerly known as Google AdWords) or Bing Ads. Within these platforms, advertisers create campaigns, ad groups, and ads. They set targeting options, including location, language, device, and demographics.
3 – Ad Auctions
When a user enters a search query, search engines run an auction to determine which ads to display. The auction considers factors such as the bid amount, ad relevance, landing page quality, and expected click-through rate (CTR).
4 – Ad Formats
SEM ads typically appear above or below organic search results, marked as “sponsored” or “ad.” Ad formats can include text ads, shopping ads (for e-commerce), image ads, video ads, and app promotion ads.
5 – Bidding Strategies
Advertisers set bids for their chosen keywords, which represent the maximum amount they are willing to pay when a user clicks on their ad. Bidding strategies may include manual bidding, automated bidding, or a combination of both.
6 – Ad Extensions
Advertisers can enhance their ads with extensions, which provide additional information or links. Common ad extensions include sitelinks, callouts, location extensions, call extensions, and structured snippets.
7 – Quality Score
Search engines use a quality score to evaluate the relevance and quality of ads and landing pages. A higher quality score can lead to lower costs and better ad positions. Quality score factors include ad relevance, expected CTR, and landing page experience.
8 – Tracking and Analytics
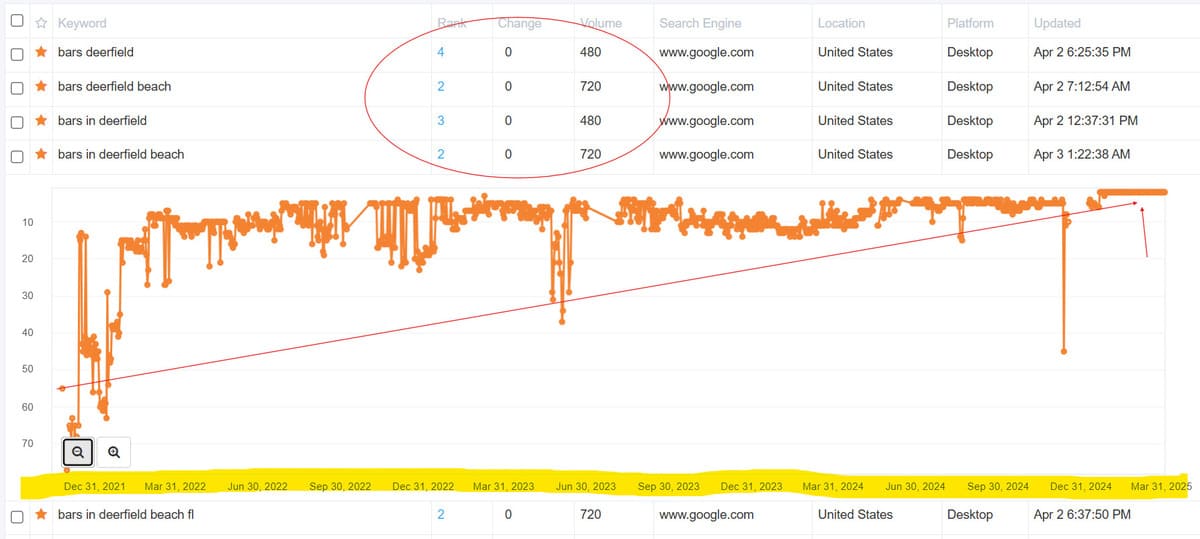
SEM campaigns should be tracked and analyzed to measure performance and ROI. Key metrics include click-through rate (CTR), conversion rate, cost per click (CPC), cost per acquisition (CPA), and return on ad spend (ROAS). Tracking can be done using platform-specific tracking tools, Google Analytics, or third-party analytics tools.
SEM is a dynamic and competitive field that requires ongoing optimization and management to achieve success. Advertisers must continuously monitor and refine their campaigns to improve performance, maximize ROI, and stay ahead of competitors.